In every organization, there are different levels of employee designation. Each designation or role has different access permissions, which administrators set.
For example, only managerial-level users may access confidential employee performance reports, while only top-level employees may access certain documents.
What are Roles and Privileges?
A role or privilege is a set of permissions an administrator grants to a user or user group. Access is granted based on the user’s position, authority, and responsibility. For example:
➤ Only developers should have access to the source code, while testers should not.
➤ Users working in development should not have access to leads and competitor reports.
➤ Users working on specific projects should only have access to those projects.
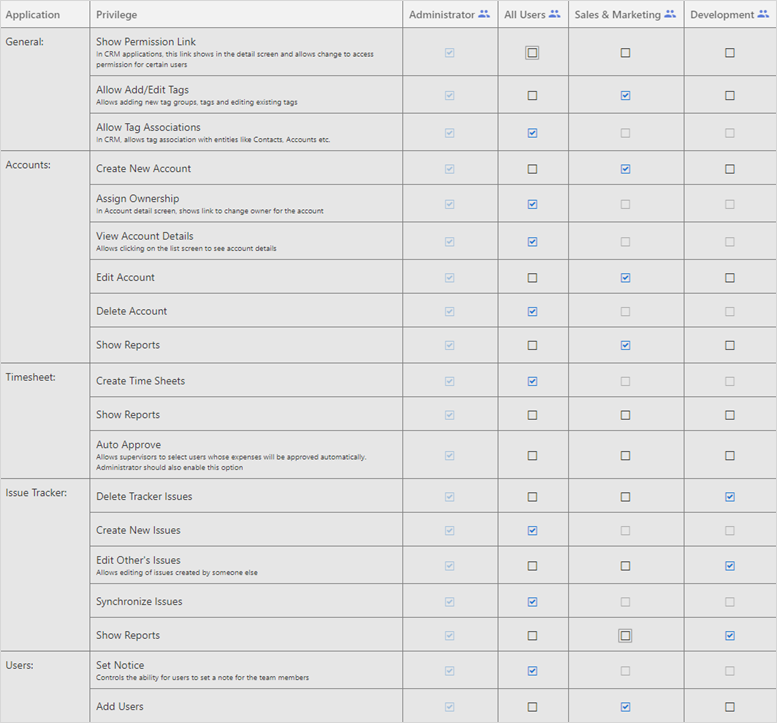
Roles and Permissions: Who sets them and why?
Administrators can set permissions for users to view reports, documents, and other data. They can also set permissions to determine which department users can access what kind of data. For example, permissions can be set to allow users to:
- Add, edit, or delete contacts, accounts, or opportunities
- Edit or delete timesheets
- View timesheets
- View certain timesheet reports
- View documents
- View reports that track time for different tasks
Role-Based Access Control helps to secure sensitive organizational information. By limiting access to data to only those users who need it, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. Additionally, these controls can help to improve efficiency by ensuring that users only have access to the data they need to do their jobs.
Conclusion:
Setting role-based access control is a critical security measure that can help organizations to protect their data and improve efficiency. Administrators can ensure that users can only access the data required by carefully defining roles and privileges.

